Refrences » Time Synchronization in Electrical Systems
Precise Time Synchronization for Substation Automation purposes.

What is time synchronization and how does it work? Which solutions exist for power transmission and distribution systems? What is precision, accuracy and resolution and why should manufacturers and operators of equipment for electrical distribution networks care about these terms? This document has been created to answer these questions and offers you a comprehensive and easy-to-understand introduction. Read on ...
- Time Synchronization Overview
- Time Synchronization Equipment
- Examples of use
- Time Synchronization Terms and Glossary
Time Synchronization Overview
Substation automation demands precise time synchronization for a variety of Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs). There are different possible approaches to achieve the required accuracy. Time synchronization for substations with integrated protection- and system control functions, as well as data collection require a target architecture that distributes synchronized time in several ways. Different solutions are possible and can be realized using MEINBERG timing equipment.
Electrical companies are turning into the biggest users and generators of
- Operational Data
- Administrative Data
- of real time data
- Operational data
- SCADAs-> Protocolization and registration
- Communication equipment-> Communication processors, protocol translators
- Protection relays-> Fault and performance analysis
- Faultrecorders-> Post mortem analysis, responsability, liability
- Billingmeters AMR-> Tarifswitching, load analysis
- IEDs, RTUs, SOE, Sensors-> Protocolization + registration
- Servers, Routers, Switches-> IT security!
- Frequency deviation-> Systemstability
- Security monitoring-> Physical security
- Digital voice and video recording-> Civil responsability, Law, Insurance companies
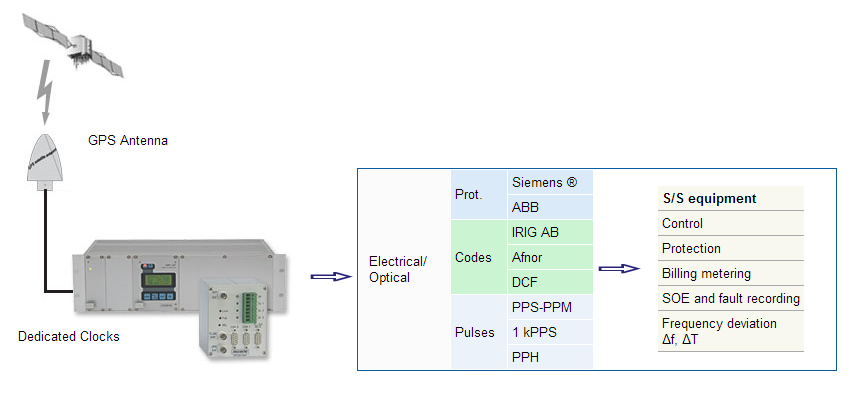
Synchronization of Equipment
Direct Synchronization
Syncronization over LAN
Resolution and Precision:
- Depends on traffic on the network
- Depends on distance and communication media
- Range from submiliseconds to 5 -20 ms
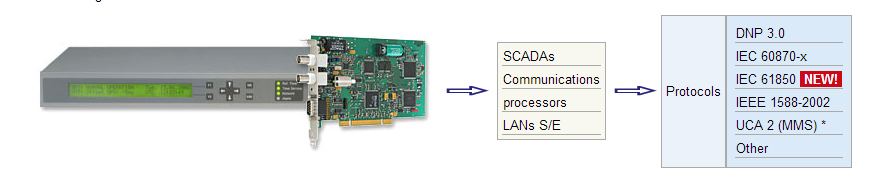
* UCA2 (Utility Communication Architecture) with MMS protocol(Manufacturing Message Specification)
Synchronization over LAN
- External networks are gaining more significance in control and protection environments through:
- LAN, WAN, MAN
- Redundant LANs
- Switches, routers, firewalls
- Severs and clients
- Communication over Internet and Intranets
- Different medias
- Transmission of secure data on insecure channel:
- Confidenciality
- Integrity
- Authentication
- Tools:
- Encrypted tunnels
- VPN
Synchronization Equipment from Meinberg
- Clocks for SCADAs, RTUs, PLCs, relays, automation
- PPH, PPM, PPS
- Optical outputs
- DCF, IRIG A/B Codes, etc.
- Proprietary codes: SIEMENS, ABB, ION etc.
- Frequencies/Amplitudes: Fixed and variable
- Frequency measurement
- PCI cards
- Special signals and interfaces
- Slave clocks
- Wide AC and DC power supply ranges
- Mounting on 19" Rack, DIN rail
- Antenna with cable up to 300 meters, optical available
Examples of Use
- Time Synchronization with GPS170BGT - LAN-CPU
- Time Synchronization with customized GPS170BGT
- Time Synchronization with GPS-Signal Distributor
Time Synchronization with GPS Satelllite Clock and LAN-CPU in Modular Case
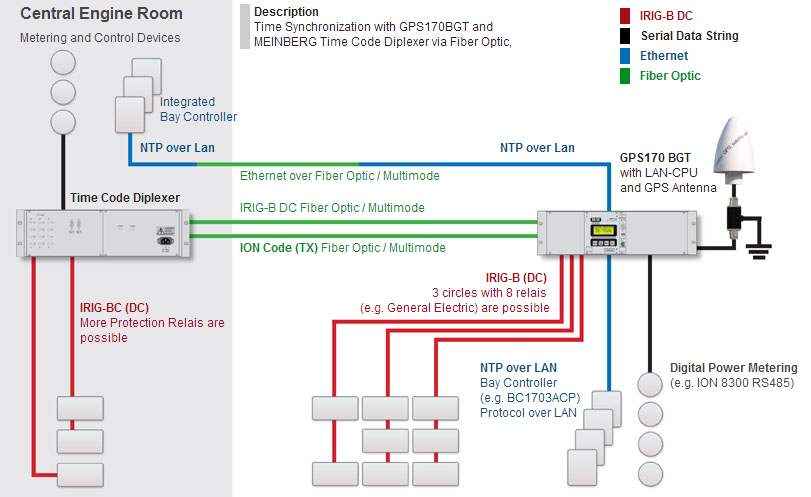
Time Synchronization with customized GPS Satellite Timing System
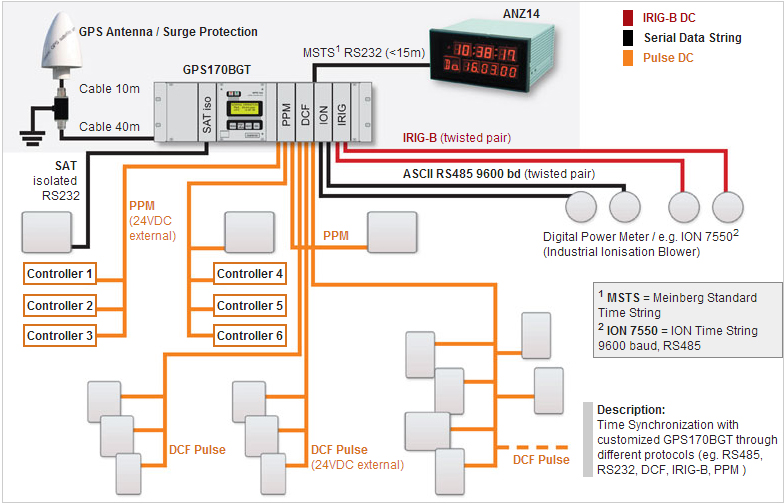
Time Synchronization with GPS-Antenna Distributor GPSAV4

Time Synchronization Terms and Glossary
What is Accuracy?Accuracy (Precision)
|
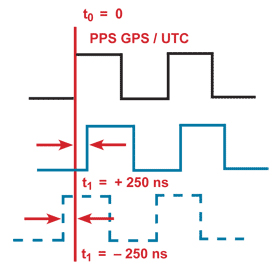 |
What is Resolution?
|
|
Usual signals for time synchronization in electrical systems:
Each signal type has its own resolutione.g. IRIG-B: The framerate is 1.0 second - but accuracies up to 1 μs can be achieved
StabilityA "free running clock" what does it mean?
|
|


